ES6入门
前言:万丈高楼平地起,打牢基础是根本
ES6官网:https://262.ecma-international.org/6.0/
ES谢成老师总结:http://es.xiecheng.live/
什么是ES6?和JS有什么关系?
ES是一种标准,可以说规定了一些东西,比如语法啊之类的。然后JS是对这种标准的实现。ES6中的6是版本号,对应ES2015,每年都会有新的标准。
总体框架——ES6中最特别的三个特性
工欲善其事必先利其器
- VSCode
- VSCode插件:live server
- Chrome浏览器
Const
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// var es = 'es6';
// es = 'es2015';
// console.log(es);
// ES3的情况下声明的常量
// var BASE_URL = 'https://www.google.com';
// console.log(BASE_URL);
// ES5的情况下声明的常量
// Object.defineProperty(window, 'es', {
// value: 'es6',
// writable: false
// });
// console.log(es);
// es = 'es2015';
// console.log(es);
// ES6的情况下声明的常量
// 使用const声明
// const es = 'es6';
// console.log(es);
// es = 'es2015';
// console.log(es);
// const一开始声明的变量就要赋初始值,不然会报错
// const es;
// es = 'es6';
// var可以重复声明
// var str = 'es6';
// var str = 'es2015';
// console.log(str);
// const声明的常量不允许重复声明
// const str = 'es6';
// const str = 'es2015';
// console.log(str);
// var声明的变量 属于 顶层对象window的
// var str = 'es6';
// console.log(str);
// console.log(window.str);
// const声明的变量 不属于 顶层对象window的;undefined
// const str = 'es6';
// console.log(window.str);
// 这种是好的,如果随着变量声明的变多,都属于顶层对象的话,就会混乱,称污染全局
// const就避免了这种情况
// 变量提升
// 这样写
// console.log(str);
// var str = 'es6';
// 相当于
// var str;
// console.log(str);
// str = 'es6';
// const 不存在变量提升;安全;要先定义,后调用。
// console.log(str);
// const str = 'es6';
// if (true) {
// var str = 'es6';
// }
// console.log(str);
// const 块级作用域
// if(true){
// const str = 'es6';
// }
// console.log(str);
// const esObj = {
// name: 'es6',
// year: '2015'
// };
// // Object.freeze(esObj); 使用freeze冻结,里面的内容就不能被改变
// esObj.name = 'es2015';
// console.log(esObj);
// const arr = ['es6', 'es7', 'es8'];
// // Object.freeze(arr);
// arr[0] = 'es2015';
// console.log(arr);
// 准确来说 const 声明的是变量所存储的内容是不可以被改变的
// 内容里面可能是地址,但是不妨碍地址指向的内容的改变。
// 如果里面的内容还有数组,比如下面
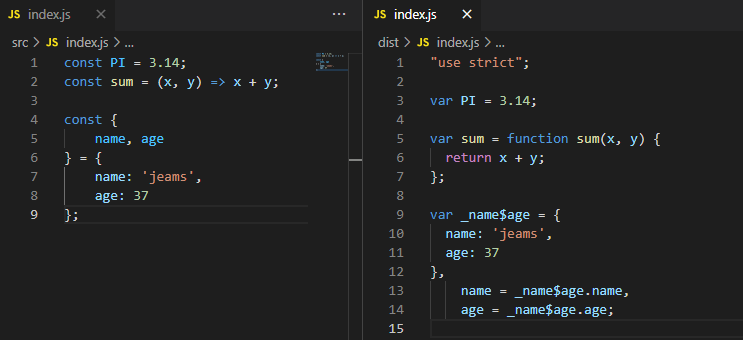
const esObj = {
name: 'es6',
year: '2015',
extension: ['es6', 'es7', 'es8']
};
// 那么freeze对于深层次的没有效果
// Object.freeze(esObj);
freezeAll(esObj);
esObj.extension[0] = 'es2015'
console.log(esObj);
function freezeAll(obj) {
Object.freeze(obj);
Object.keys(obj).forEach(function (key) {
if (typeof obj[key] === 'object') {
freezeAll(obj[key]);
}
});
}
// 现在声明变量用let,不要用var;声明常量用const
// 优先用const来写
</script>
</body>
</html>Arrow Function
函数的更加简单的写法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<button id="btn">
我是按钮
</button>
<script>
// function sum(x, y) {
// return x + y;
// }
// const sum2 = function(x , y) {
// return x + y;
// };
// const res = sum(2, 3);
// console.log(res);
// const res2 = sum2(3, 4);
// console.log(res2);
// const sum3 = (x, y) => {
// return x + y;
// };
// const sum3 = (x, y) => x + y;
// const res3 = sum3(4, 5);
// console.log(res3);
// const fn = (x) => {
// // 业务逻辑代码
// }
// const fn = x => {
// // 业务逻辑代码
// }
// 找到按钮
// const oBtn = document.querySelector('#btn');
// oBtn.addEventListener('click', function(){
// console.log(this);
// this.style.backgroundColor = '#f00';
// });
// 在箭头函数里面是没有this,它会通过上层作用域链找this,上层找就会找到window
// oBtn.addEventListener('click', () => {
// console.log(this);
// this.style.backgroundColor = '#f00';
// });
// const obj = {
// name: 'jeams',
// // showName: function() {
// // console.log('我的名字是:' + this.name);
// // }
// // showName: () => {
// // consolo.log(this);
// // console.log('我的名字是:' + this.name);
// // }
// // ES6对象 简写的形式
// showName() {
// console.log('我的名字是:' + this.name);
// }
// };
// obj.showName();
// function sum4(x, y) {
// console.log(arguments);
// }
// sum4(2, 3);
// 箭头函数里不能用arguments
// const sum5 = (x, y) => {
// console.log(arguments);
// return x + y;
// };
// sum5(3, 4);
// 类 ES5的语法
function Course(name, price) {
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
Course.prototype.study = function() {
console.log(`我要学习${this.name}, 价格是:${this.price}`);
};
// 不能使用箭头函数作为构造函数
// const Course = (name, price) => {
// this.name = name;
// this.price = price;
// }
// 也不能作为原型方法
// Course.prototype.study = () => {
// console.log(`我要学习${this.name}, 价格是:${this.price}`);
// };
const c1 = new Course('es', 500);
console.log(c1);
c1.study();
</script>
</body>
</html>Destructuring
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/axios/0.24.0/axios.js"></script>
<script>
// 更加优雅的取值方式
// 解构赋值
// const course = {
// name: 'es6',
// price: 500
// };
// 普通方式
// const name = course.name;
// const price = course.price;
// 解构方式——关于对象的
// const {name, price} = course;
// console.log(name, price);
// const courseArr = ['es6', 'es7', 'es8'];
// const a = courseArr[0];
// const b = courseArr[1];
// const c = courseArr[2];
// const [a, b, c] =
// console.log(a, b, c);
// const course = {
// name: 'es6',
// price: 500,
// teacher: {
// name: 'jeams',
// age: 37
// }
// };
// 取值,有两个name,如何不冲突?
// const {
// name: courseName, // 别名 courseName
// price,
// teacher: {name, age}
// } = course;
// console.log(courseName, price, name, age);
// 使用数组的时候用解构赋值可以更加灵活
// 未使用解构
// const sum = arr => {
// let result = 0;
// for(let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
// result += arr[i];
// }
// console.log(result);
// };
// 使用解构
// const sum = ([a, b, c]) => {
// console.log(a + b + c);
// };
// sum([1, 2, 3]);
// 解构赋值正确的使用姿势
// const fun = ({name, age, school = 'XX学校'}) => {
// console.log(name, age, school);
// };
// fun({
// name: '张三',
// age: 20,
// school: 'imooc'
// })
// const fun = () => {
// return {
// name: '张三',
// age: 20
// }
// };
// const {name, age} = fun();
// console.log(name, age);
// let a = 1;
// let b = 2;
// // 交换
// [b, a] = [a, b];
// console.log(a, b);
// json
// const json = '{"name": "es", "price": "500"}';
// // const obj = JSON.parse(json); // 把字符串转成对象
// // console.log(obj);
// const {name, price} = JSON.parse(json);
// console.log(name, price);
// 引入axios的js库,可以搜索axios cdn找到相关链接
// axios.get('./data.json').then(function(res) {
// console.log(res);
// });
// 可以用箭头函数
axios.get('./data.json').then(res => {
console.log(res);
});
// 可以解构
axios.get('./data.json').then(({data}) => {
console.log(data);
});
axios.get('./data.json').then(({data: {name, type}}) => {
console.log(name, type);
});
</script>
</body>
</html>同目录下随便写的data.json
{
"name": "es6",
"type": "前端"
}兼容ES5的浏览器
当我们用ES6的标准来写js,之后可能有的浏览器不支持ES6,只支持ES5这种,那么就需要通过一个工具来转化,这个工具就是Babel
安装Node.js环境:https://nodejs.org/zh-cn/
进入到项目,初始化package.json:
npm init -y安装
npm install --save-dev @babel/cli @babel/core @babel/preset-env创建文件并配置:.babelrc
自己找个地方,建个文件夹,我这里创建了一个叫ES_BABEL的文件夹,就当我们的项目。我们项目的根目录,在VSCode中打开这个目录。
VSCode中打开终端的方法:Ctrl + ~
可查看node是否安装成功,输出node版本号
node -v初始化
npm init -y初始化后会自动生成package.json
{
"name": "ES6_BABEL",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1"
},
"keywords": [],
"author": "",
"license": "ISC"
}通过npm安装需要的两个包
npm install --save-dev @babel/cli @babel/core @babel/preset-env编写.babelrc文件,要通过VSCode编写,因为Windows下默认不能新建没有文件名的文件
{
"presets": ["@babel/preset-env"]
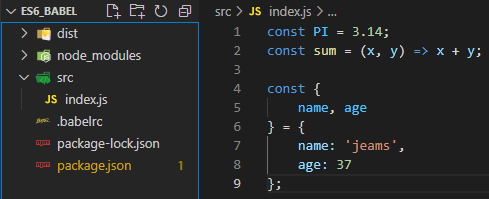
}然后搞多两个文件夹,一个是src,另一个是dist。src用来写ES6标准的js,dist用来存放转化后的js的。
同时在src下随便写下ES6标准的js
完成后整体目录结构是这样的。
文件转化命令
文件
babel src/index.js -o dist/index.js文件夹
babel src -d dist实时监控
babel src -w -d dist
转化后如下: